One-Sentence Definition
The Rho Index measures the degree to which asset or portfolio returns are associated with changes in interest rates over a defined period.
What It Measures
- Interest-rate sensitivity: how returns tend to move as rates rise or fall.
- Directional exposure: whether rate changes historically correspond to positive or negative performance.
- Strength of relationship: the magnitude and stability of the rate–return association.
Where It’s Used
- Portfolio analysis: assessing rate exposure across asset classes.
- Macroeconomic research: studying market response to monetary policy shifts.
- Risk management: identifying sensitivity to tightening or easing cycles.
- Benchmarking: comparing interest-rate dependence across time or strategies.
Why an Index Matters
Interest rates affect many assets indirectly and with varying lag. A standardized index provides a shared reference for describing that sensitivity, improving clarity when comparing results across periods, portfolios, or studies.
Example: Rolling 12-Month Rho
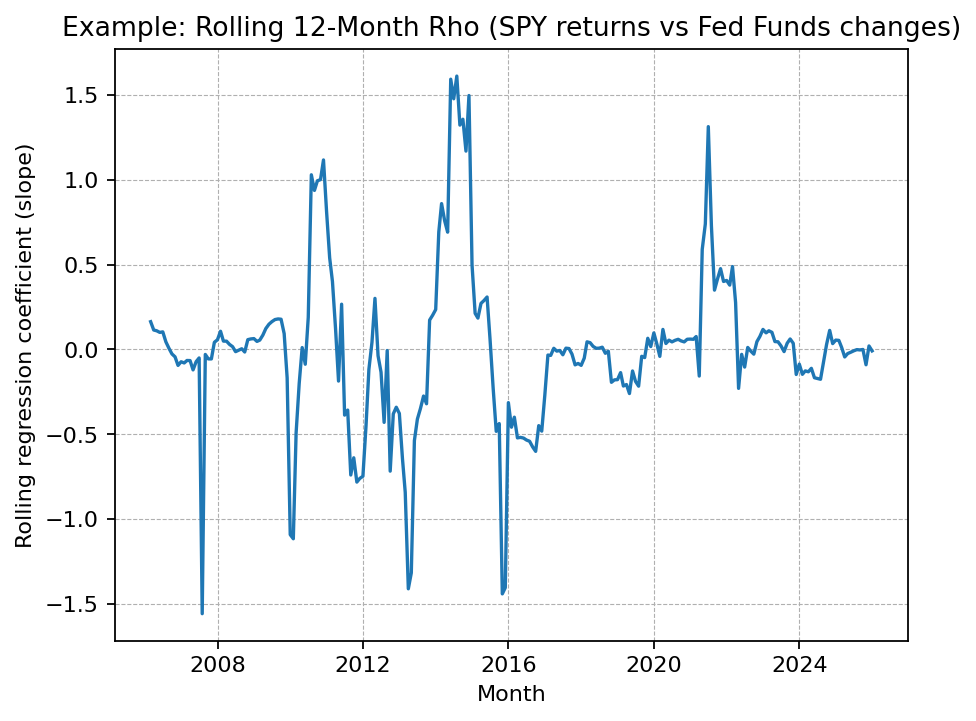
Chart updated daily using public data sources.
Scope & Terminology Note
“Rho” is used in multiple disciplines, including statistics and options pricing. This page refers specifically to a rate-sensitivity index concept, not any proprietary product, formula, or trading signal.